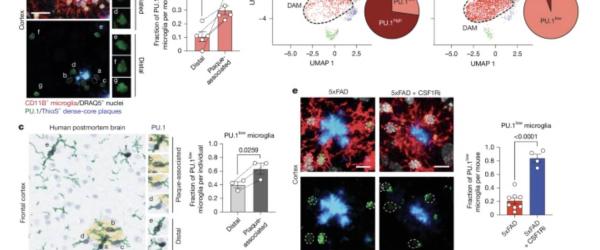
A study (link) involving the SynapTau team has just been published open access in Nature. It shows that microglia, the brain’s innate immune cells, play a crucial role in the progression of Alzheimer’s disease, and that their protective function is controlled by the transcription factor PU.1, which is downregulated following contact with amyloid plaques.
Image